更新時間:2022-11-22 09:03:03 來源:動力節點 瀏覽1558次
套接字是一種軟件(邏輯)端點,它在服務器和一個或多個客戶端程序之間建立雙向通信。套接字綁定到端口號,以便 TCP 層可以識別數據要發送到的應用程序。應用程序軟件定義了一個套接字,以便它利用底層計算機中的端口來實現它。這使程序員能夠在其應用程序代碼中輕松處理網絡通信的低級細節,例如端口、路由等。
客戶端和服務器之間的 TCP 套接字通信由幾個階段組成。
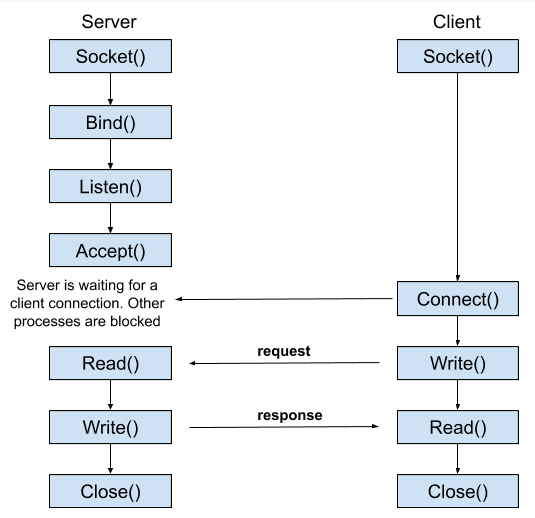
在開始研究文件傳輸之前,讓我們看看如何在 Java 中實現套接字通信。在這里,我們將編寫兩個 Java 程序。一個是在服務器上運行的程序,另一個是將與服務器通信的客戶端程序。
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
private static DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null;
private static DataInputStream dataInputStream = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(5000)){
System.out.println("listening to port:5000");
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println(clientSocket+" connected\n");
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(clientSocket.getInputStream());
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(clientSocket.getOutputStream());
String message;
while (true) {
message = dataInputStream.readUTF();
System.out.println(message);
if(message.equalsIgnoreCase("exit()"))
break;
}
clientSocket.close();
} catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
在這里,ServerSocket 在本地機器的 5000 端口打開一個套接字并等待客戶端,server.accept()接受傳入的客戶端連接。
連接客戶端后,將實例化輸出和輸入流,可用于使用流提供的方法之一與連接的客戶端進行read通信write。
在上面的程序中,服務器循環并接受來自客戶端的字符串輸入,dataInputStream.readUTF()然后將其打印在控制臺上,并在接收到的輸入為exit().
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Client {
private static DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null;
private static DataInputStream dataInputStream = null;
private static Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",5000)){
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
while (true) {
System.out.print("input> ");
String message = scanner.nextLine();
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(message);
if(message.equalsIgnoreCase("exit()"))
break;
}
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
在這里,Socket 將客戶端應用程序連接到在 localhost:5000 偵聽的上述服務器,在連接被接受后輸出和輸入流被實例化。
該程序接受來自控制臺的字符串輸入,然后使用 將其發送到服務器,dataOutputStream.writeUTF()并在掃描的輸入匹配時退出循環exit()。
運行程序:
首先,運行Server.java程序,然后運行Client.java程序。您將在服務器端看到連接已接受消息,客戶端將接受輸入。客戶端鍵入的輸入將在服務器端回顯,以exit()在打破while(true)循環的客戶端應用程序中退出類型。
如果你做到了這一步,你就已經獲得了足夠的知識來完成任務。
文件傳輸會像這樣簡單:
void sendFile(String filePath){
byte[] buffer = new byte[Integer.MAX_VALUE];
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(文件路徑);
int bytes = fileInputStream.read(buffer,0,buffer.length);
dataOutputStream.write(buffer,0,bytes);
}
void receiveFile(String newFileName){
byte[] buffer = new byte[Integer.MAX_VALUE];
int bytes = dataInputStream.read(buffer,0,buffer.length);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(newFileName);
fileOutputStream.write(buffer,0,bytes);
}
但是這段代碼有兩個主要問題。
文件大小:
有人可能會說,如果文件大小大于Integer.MAX_VALUE字節,即 2GB,如果是這種情況,這就足夠了。
真正的問題是套接字一次只允許 65482 字節,即 64KB,這比上傳到上的大多數文檔文件大小要小得多網。
多個文件:
即使文件小于 64KB,此代碼的另一個問題是在發送多個文件并檢測 EOF 時,發送方不會有任何問題,因為fileInputStream.read()它隱式地用于打開的文件(因為 EOF 導致流結束本身)。
但是在從多個文件接收數據的接收端,dataInputStream一個接一個地排隊,并且沒有任何方法可以分別檢測每個文件的 EOF,因此,它將讀取排隊的整個字節作為一個文件。fileOutputStream.write(buffer)當檢測到第一個文件的 EOF 并且剩余文件丟失時,使用寫入停止寫入此字節緩沖區。
因此,上述代碼僅適用于大小小于 64KB 的單個文件。
文件大小:這個問題的一個明顯解決方案是將文件分成多個塊,比如 4KB,然后在循環語句中通過套接字發送它們,并以類似的方式接收,即wile(stream.read(buffer)!=-1){ ... }
多個文件:這個問題的主要原因是我們不知道接收到的字節中每個文件的 EOF dataInputStream,這可以通過在發送每個文件之前發送文件大小(以字節為單位)來解決,因此我們可以從dataInputStream之后中斷讀取文件大小并對字節緩沖區中排隊的剩余文件重復相同的操作。
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Client {
private static DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null;
private static DataInputStream dataInputStream = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",5000)) {
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
sendFile("path/to/file1.pdf");
sendFile("path/to/file2.pdf");
dataInputStream.close();
dataInputStream.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void sendFile(String path) throws Exception{
int bytes = 0;
File file = new File(path);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// send file size
dataOutputStream.writeLong(file.length());
// break file into chunks
byte[] buffer = new byte[4*1024];
while ((bytes=fileInputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
dataOutputStream.write(buffer,0,bytes);
dataOutputStream.flush();
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
文件發送者
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
private static DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = null;
private static DataInputStream dataInputStream = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(5000)){
System.out.println("listening to port:5000");
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println(clientSocket+" connected.");
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(clientSocket.getInputStream());
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(clientSocket.getOutputStream());
receiveFile("NewFile1.pdf");
receiveFile("NewFile2.pdf");
dataInputStream.close();
dataOutputStream.close();
clientSocket.close();
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void receiveFile(String fileName) throws Exception{
int bytes = 0;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(fileName);
long size = dataInputStream.readLong(); // read file size
byte[] buffer = new byte[4*1024];
while (size > 0 && (bytes = dataInputStream.read(buffer, 0, (int)Math.min(buffer.length, size))) != -1) {
fileOutputStream.write(buffer,0,bytes);
size -= bytes; // read upto file size
}
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
文件接收器
 Java實驗班
Java實驗班
0基礎 0學費 15天面授
 Java就業班
Java就業班
有基礎 直達就業
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
業余時間 高薪轉行
 Java在職加薪班
Java在職加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架構師班
Java架構師班
工作3~5年,晉升架構
提交申請后,顧問老師會電話與您溝通安排學習